Identify suspected counterfeit products and unknowns in finished and raw materials
Counterfeit Analysis Programs
In recent years, the number of counterfeit drugs has increased dramatically, including not only "lifestyle" products but also vital medicines. In addition to the threat to public health, the financial and reputation damage to pharmaceutical companies is substantial. The lack of robust information on the prevalence of fake drugs is an obstacle in the fight against drug counterfeiting. It is generally accepted that approximately 10% of drugs worldwide could be counterfeit, but it is also well known that this number covers very different situations depending on the country, the places where the drugs are purchased, and the definition of what constitutes a counterfeit drug.1
The International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Associations (IFPMA) has estimated that >10% of all drugs sold around the world are counterfeits. More than 50% of medicines purchased worldwide from illegal online sources are counterfeit. They have suggested that the value of this trade is more than USD 50 billion. In Russia, the figure has been put at 12% while in the Ukraine it may be as high as 40%. Of 81 countries inspected by Interpol, 48 were identified as sources of counterfeit products in 2011.2 The WHO has indicated that India is responsible for about 35% of the world’s counterfeit medicines with the business being worth more than USD 200 million annually.
The chemical analysis of drugs suspected to be fake is a crucial step as counterfeiters are becoming increasingly sophisticated, rendering visual inspection insufficient to distinguish the genuine products from the counterfeit ones.
Triclinic Labs has extensive experience in the identification of counterfeit products (packaging, labeling, drug substances, drug products, medical devices). Our unique combination of analytical techniques, spectral libraries, and industry experience allows us to develop strategies to not only accurately identify counterfeit items but also catalog and mitigate the strategies and tactics employed by counterfeiters. For more information on our comprehensive counterfeit programs please contact us.
1. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Sep;398(1):77-92. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3748-y. Epub 2010 May 1
2. https://www.ifpma.org/
3. WHO factsheets https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs275/en

Counterfeit Analysis Capabilities - Patient Complaint Analysis Specialists
-
Labels
- Gross Analysis (Color, Placement)
- Paper
- Ink
- Spacial Authenticity
-
Adhesive
-
Packaging
- Container Dimensional Size and Accuracy
- Polymer Identification and Composition
- Induction Seal Integrity
- Adhesives
-
Residue Analysis
-
Drug Product Analysis
- Active Ingredient Identification and Confirmation
- Potency
- Excipient Distribution and Authenticity
- Others
See below for data examples.
Contaminant, and Foreign Material Identification
If you have an unknown substance we can quickly and confidently help identify the material. We specialize in pharmaceutical and fine chemical contaminant analysis and foreign material identification.
We have expertise in analysis of:
- Failures
- OOS
- Contaminants
Pharmaceutical contamination testing and identification projects at Triclinic Labs involve off-color investigations as well as foreign materials in a product. Sources of contaminants include the environment, improper storage of the product, poor quality raw materials, items introduced during manufacturing including those from an undetected change in the process (e.g. polymorphic conversion), and unexpected sources. We work quickly and closely with you to determine the source of contamination and develop a corrective action program.

Figure 1. Analysis of a contaminant found in raw material. Optical microscopy and subsequent spectral analysis confirms the material is cotton fiber. False color SEM. For more information on microscopy and imaging please click here.
| Typically Utilized Contaminant Analysis Techniques |
|
RAMAN and
IR
Microscopy
Chemical imaging and micro and macro product mapping, matching to spectral libraries of authentic materials. Learn more about spectroscopic techniques, click here. |
|
Scanning Electron Microscopy & CryoSEM
Analyze hydrated samples. Learn more about SEM techniques, click here. |
|
SEM/Electron Dispersive X-Ray
Micro Elemental Analysis. Learn more about elemental analysis techniques, click here. |
|
Optical and Digital Microscopy
Still and dynamic image capturing. Learn more about microscopy techniques, click here. |
|
FT-IR with ATR,
Diffuse reflectance, transmission, gas cell, matching to spectral libraries. Learn more about spectroscopic techniques, click here. |
|
Mass Spectrometry
GC/MS, LC/MS, LC/MS/MS and MALDI, matching to libraries - chemical identification. Learn more about MS techniques, click here. |

Application Notes:
Identification of Cellulosic Fibers by Infrared Spectroscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy
This application note demonstrates how scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can be used in conjunction with Infrared (IR) micro spectroscopy to identify different cellulosic fibers based on surface features and overall fiber appearance.Download the application note!
Mini Case Study #1.
Goal: Determine whether a submitted final dosage container is authentic or possibly a counterfeit. A multi-disciplinary approach was used: Visual inspection, Optical microscopy, Infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy.

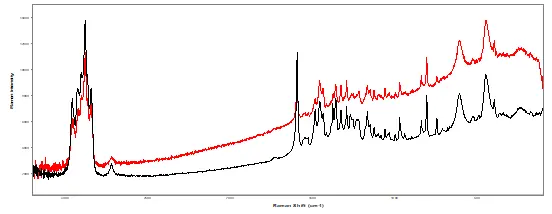
Figure 2. Comparison of the ink application for a section of the suspect (top) versus authentic (bottom) label. Raman Spectral comparison of ink on both (black) authentic and (red) suspect labels (bottom spectrum).
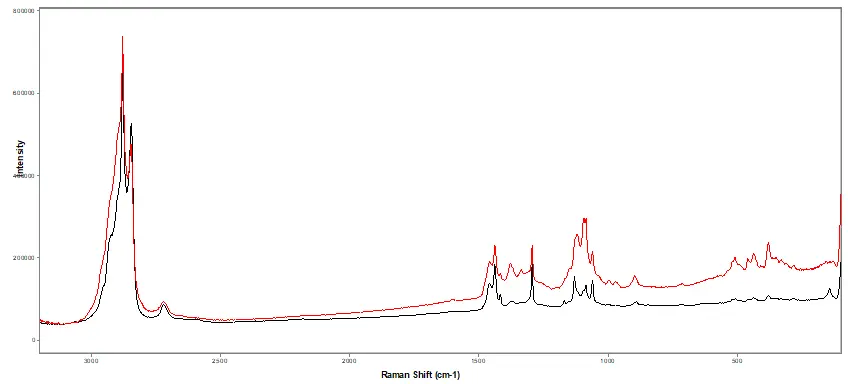 Figure 3.
Induction seal IR spectral comparison comparison of both (black) authentic and (red) suspect seals.
Figure 3.
Induction seal IR spectral comparison comparison of both (black) authentic and (red) suspect seals.
Conclusion: Authentic Materials; production run variations in packaging caused by using a different printing company were the source of differences. A multi-disciplinary approach was used:
- Multiple aspects of the label, container, and seal used to determine authenticity
- Establish basis sets for authentic materials
Mini Case Study #2.
Goal: Identify suspect tablets as authentic or counterfeit. An open container of final dosage product was submitted in which three tablets appeared suspect. Physical measurements and color of the tablets showed that they were not authentic.
- Visual Comparison; Suspect Tablets vs. Authentic Reference
- Embossing: None versus "xxx" on one side, "xxxx" on the other side for authentic
- Physical size: 19 x 10 mm versus 14.48 mm length, 10.51 mm width, 5.59 mm height
Chemical Identification was performed to attempt to identify the chemical components of the suspect tablet.
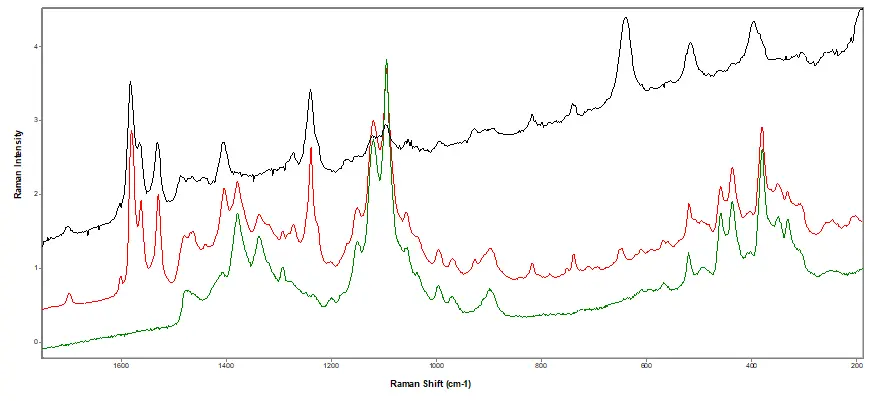 Figure 4.
Raman Spectral Analysis. Black: library spectrum of Pfizer's Viagra. Red: suspect tablet. Green: library
spectrum of microcrystalline cellulose.
Figure 4.
Raman Spectral Analysis. Black: library spectrum of Pfizer's Viagra. Red: suspect tablet. Green: library
spectrum of microcrystalline cellulose.
Conclusion: Counterfeit tablets. A multi-disciplinary approach was used:
- Counterfeit tablets identified as sildenafil citrate (active in Viagra) with MCC and titanium dioxide.
- Visual inspection: Color: Pink versus orange (brand color), tablet measurement, and comparison to reference authentic materials.
- Raman spectroscopy with spectral library matching.

Download The Publication Entitled "Chemical Identity Testing" In Applied Spectroscopy by David E. Bugay, Ph.D
See What Help We Offer Consumers:


