Chemical and Material Composition Analysis
Drug coating inconsistencies, microscopic cracks, alloy mix-ups, or trace-metal contamination can derail a
510(k) or spark a costly recall. Our lab pinpoints these issues with a full array of techniques and
expertise — so you can fix them before the FDA asks. Get results in as little as 24 hours!
Areas of Expertise:
| Test Category | Typical Methods | What the Data Prove |
| Chemical & Material Composition |
• FT-IR / Raman • Thermal analysis: DSC / TGA • X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) — phase ID • SEM-EDS — microstructure & inclusions • ICP-MS/OES — elemental impurities |
Confirms resin grade, alloy or ceramic phase, and detects contaminants that could drive biocompatibility risk assessments. |
| Extractables / Leachables & Residuals |
• Headspace GC/MS & LC/MS for organic profiles • ICP-MS for trace metals |
Shows that patient-contact devices (catheters, wearables, drug-device combos) will not release harmful chemicals during their use life. |
| Particulate & Cleanliness |
• Non-volatile-residue gravimetry • SEM-EDS/XPS for particle ID • Light microscopy / ICC particle counting |
Verifies that manufacturing debris, machining oil, or residue remain within accepted limits and identifies particulate & cleanliness failures during production or packaging. Identify contaminants. |
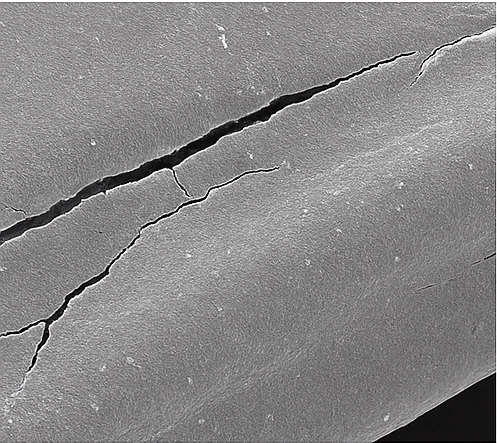
Device Analysis Techniques:
| Technique | What you get | Typical Use-cases |
| SEM metrology (20 nm resolution) | Surface-defect imaging, dimensional checks (± 0.05 µm) | Stent strut cracks, catheter-balloon wrinkles; verifying critical tolerances |
| EDX elemental mapping | Alloy verification, plating-thickness, foreign-particle ID | Nitinol/titanium homogeneity, solder inclusion |
| ICP-MS trace-metals | Quantitation to ppb; USP <232>/<233> style | Ni, Cr, Co leachables; contamination audits |
| GC/MS, LC/MS, LC-MS/MS | Sensitivity to low-ppb; structural confirmation via MS/MS; broad organic coverage | Detects plasticizers, antioxidants, oligomers, residual monomers in extractables/leachables studies |
| XRPD phase ID | Crystal-structure & polymorph identification; amorphous vs crystalline quantitation | Detects phase changes in drug-eluting coatings; verifies ceramic phases in orthopedic implants; confirms lot-to-lot raw-material consistency |
| FT-IR infrared spectroscopy | Chemical-bond fingerprint; functional-group verification | Rapid polymer/resin ID, silicone-residue confirmation, monitoring oxidation or cross-linking of catheter materials |

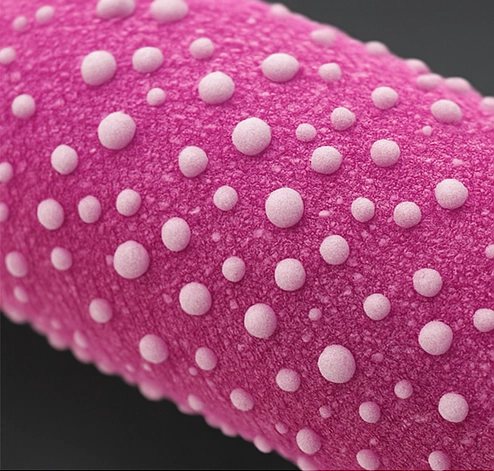
Drug-Coated Medical Device Analysis
Comprehensive characterization, stability & release profiling for drug-eluting stents, balloons, catheters, and combination products. We have extensive experience in analyzing material deposition and consistency.
Stay compliant—and competitive
Regulators expect robust, multi-technique evidence that your coating is uniform, adherent, chemically intact, and releases its payload at the intended rate. Triclinic Labs pairs advanced surface, structural, and compositional analyses with cGMP data packages to keep your submission on track and your product performing in the field.
| Test Category | Typical Methods | What the Data Prove | |
| Coating Uniformity & Thickness |
• Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) • Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) • Optical/Confocal Profilometry |
Is the drug layer continuous? What is the thickness distribution along critical features? | |
| Drug Identity & Crystalline Form |
• X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) • Micro-Raman & FT-IR Spectroscopy • Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) |
Has polymorphic form changed during processing or sterilization? | |
| Drug Loading & Content Uniformity |
• HPLC/UPLC with UV or MS detection • LC-MS/MS quantitation • ICP-MS (for metallic APIs or excipients) |
How much API is truly on each device—and is it consistent lot-to-lot? | |
| Stability & Compatibility |
• Forced degradation analysis - LC-MS • Extractables/Leachables by GC-MS & LC-MS |
Shows manufacturing debris, machining oil or residues are within accepted limits. |

Regulatory Alignment
-
FDA Quality System Regulation (21 CFR 820) traceability
-
USP <232>/<233> elemental impurity requirements
-
Zero Form 483 observations in all FDA audits (most recent 2024)
