Achieve pharmaceutical quality through characterization, control, stability, composition.
Current Guidance for Pharmaceutical Quality/CMC
Under current regulations in the United States, use of a human drug product not previously authorized for marketing in the United States requires the submission of an IND to the Agency. FDA’s regulations at 21 CFR 312.22 and 312.23, respectively, contain the general principles underlying the IND submission and the general requirements for content and format. Section 312.23(a)(7)(i) requires that an IND for each phase of investigation include sufficient CMC information to ensure the proper identity, strength or potency, quality, and purity of the drug substance and drug product.
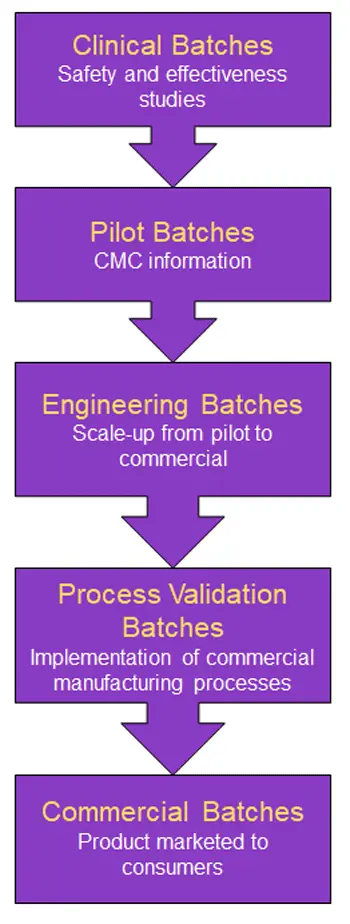
The type of information submitted will depend on the phase of the investigation, the extent of the human study, the duration of the investigation, the nature and source of the drug substance, and the drug product dosage form.
As clinical development of the drug product proceeds, sponsors can discuss with the Agency the type of CMC information that would be submitted to support the use of the drug in all investigational phases. The FDA encourages sponsors to meet with the CMC review team, if appropriate, before the initiation of or during phase 3 clinical trials to discuss issues and protocols that might affect the approvability of the NDA.Characterization
Evidence to reasonably support the proposed chemical structure of the drug substance should be provided. Data on particle size distribution and other physical properties (e.g., polymorphic or solid state form) should be generated so that relevant orrelations can be established between data generated during early and late drug development. Data on the particle size distribution and/or physical properties should be submitted, when appropriate (e.g., inhalation, suspension, modified release solid dosage forms).Updates on the information previously provided during phase 2 should be provided in information amendments. The information amendment should include evidence to support the elucidation and characterization of the structure, which augments the information provided in phase 2. This information can include elemental analysis, conformational analysis, molecular weight determination, spectra from IR, NMR (1 H & 13C), UV, MS, optical activity, and if available, single crystal X-ray diffraction data, if not previously provided. Analytical procedures used to characterize the primary reference material should also be provided in an information amendment.
Control of Drug Substance
A specification sheet is a list of tests, analytical procedures, and acceptance criteria (i.e., numerical limits, ranges, or other criteria for the tests described). Critical quality attributes include, but are not limited to, identity, purity, quality, potency or strength, and impurities. During the clinical investigation process, the sponsor would establish tentative acceptance criteria that are continually refined based on data obtained from analysis of batches of drug substance and new information that becomes available. In the course of product development, the analytical technology or methodology often evolves parallel to the clinical investigations. In setting subsequent acceptance criteria, relevant correlations should be established between data generated during early and late drug development.A detailed listing of all the tests performed on the drug substance (e.g., description, identity, assay, impurities, residual solvents) and the tentative acceptance criteria should be provided in an information amendment. A list should be provided for the testing performed by the sponsor and, if different, the drug product manufacturer. Test results and analytical data (e.g., infrared spectra, chromatograms) from batch release of representative clinical trial materials should also be provided in an information amendment initially and when any changes are made in the specification.
Stability
A description of the stability program to support the drug substance under clinical investigation in phase 2 should be submitted that includes a list of tests, analytical procedures, acceptance criteria, test time points for each of the tests, storage conditions, and the duration of the study. Description and Composition of the Drug Product
Any changes from the information specified for phase 1 (i.e., table listing of all components) should be provided. All components used in the manufacture of the drug product, regardless of whether or not they appear in the finished drug product, should be identified by their established names and a reference to a quality standard (e.g., United States Pharmacopeia (USP), National Formulary (NF)) included. The quantitative composition on a per unit basis (e.g., milligram (mg)/milliliter (mL), mg/tablet) should be provided. However, quantitative values need not be reported for components that are removed during manufacturing and do not appear in the final drug product.
Goals of CMC:
- Testing of the finished drug product alone is insufficient for control of product quality.
- The manufacturer should know which steps and variables in the manufacturing process need to be controlled and why.
- Process understanding is the foundation of a controlled manufacturing process.
Triclinic Labs can help you completely characterize your molecule, identify critical solid form parameters to control during manufacturing, trouble shoot issues with consistency, and develop crystallization methods for process control.
Goals of GMP:
- The marketed drug product is the same or similar to the product demonstrated to be safe and effective in the clinical target animal safety and effectiveness studies
- The manufacturing process consistently yields a product meeting approved quality attributes.
-
The drug product will maintain its quality attributes throughout its shelf life.
Triclinic Labs can develop and validate cGMP analytical methods for release testing to ensure comliance and consistency.
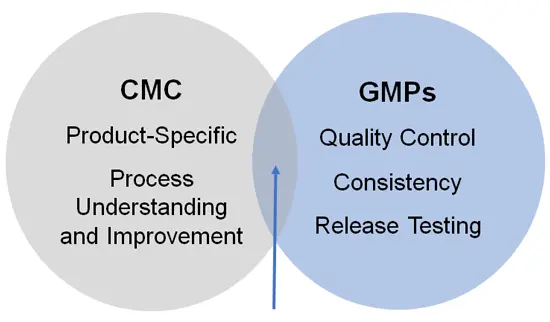 CMC review and cGMP compliance may overlap but are not the
same!
CMC review and cGMP compliance may overlap but are not the
same!
Control of Drug Product Physicochemical tests (e.g., identity, assay, content uniformity, degradants, impurities, dissolution, viscosity, particle size), biological (e.g., potency), and microbiological tests (e.g., sterility and pyrogens or bacterial endotoxins for sterile products, antimicrobial preservative for multiple-dose sterile and nonsterile dosage forms, and microbial limits for nonsterile dosage forms) that have been added or deleted from the specification 11 Contains Nonbinding Recommendations should be reported. Data on the particle size distribution and/or polymorphic form of the drug substance used in clinical trial materials should be included, when appropriate (e.g., inhalation, suspension, modified release solid dosage forms) so that relevant correlations can be established between data generated during early and late drug development and in vivo product performance. Relaxation of acceptance criteria or any change that affects safety should be reported. Test results and analytical data (e.g., chromatograms) from batch release of representative clinical trial materials should be provided initially and when any changes are made in the specification. The analytical procedure (e.g., HPLC) used to perform a test should be briefly described and changes reported when the change is such that an update of the brief description is warranted. A complete description of analytical procedures and appropriate validation data should be available for analytical procedures that are not from an FDA-recognized standard reference (e.g., official compendium, AOAC International Book of Methods), and this information should be submitted upon request.



1.https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM070567.pdf
2. Additional guidance documents (click here)
CMC Services we offer:
|
Proof of Structure
Analytical Techniques Available: |
|
|
Physiochemical Properties
Analytical Techniques Available: |
Some drug substances exist in different crystalline forms which will have different physical properties. Differences in these forms could affect the performance of the drug. If different forms exist and affect the drug, then the appropriate solid-state should be specified. |
|
CMC Specific Tests - New Drug Product
Solid Oral Tablets/Capsules: |
|
| CMC Trouble Shooting Services: |
|
Service Levels Available: