Reveal details of your chemical's molecular structure in solids and liquids
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful tool in structural identification and characterization of pharmaceuticals and other chemicals. NMR spectroscopy is used to unambiguously identify known and novel compounds. NMR is often used to satisfy the regulatory and research requirements of "identity" of a chemical or series of chemicals. NMR can be used to determine how the atoms of a particular molecule are interconnected in either the solid or liquid phase. This is done by analyzing the chemical environment of a selected atomic nucleus. All isotopes that contain an odd number of protons and/or neutrons have an intrinsic nuclear magnetic moment and angular momentum, in other words a nonzero nuclear spin, while all nuclides with even numbers of both have a total spin of zero. The most commonly used nuclei are ¹H (proton) and ¹³C (carbon).NMR spectroscopy is used to unambiguously identify known and novel compounds and much more...
| Capability Category | Primary Use / Information Gained | Key Techniques Offered | Ideal Sample Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution-State NMR | Molecular structure elucidation, purity assessment, quantitation, reaction monitoring, binding studies, cGMP method development validation, release testing |
1D ¹H, 2H,¹³C, 15N, 19F, 31P qNMR, VT-NMR, T1/T2 Relaxation time 2D (COSY, NOESY, HSQC, HMBC, DOSY) |
Soluble small molecules, peptides, natural products, polymers in solution |
| Solid-State NMR (ssNMR) | Polymorph identification, structural analysis of insoluble materials, API/excipient interactions, crystallinity |
13C, 19F, 15N, 31P, 27Al, 29Si CP/MAS, Relaxation Studies, Dipolar Coupling Analysis |
Polymorphs and amorphous materials, formulations, polymers, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, composites |
| Specialized Analyses | Problem-solving for specific R&D, QC, or regulatory requirements | Structure ID & Verification, Impurity Profiling, Formulation Characterization | Varies widely based on project needs |
NMR services Triclinic Labs offers:
| Analytical Service | Liquids - cGMP | Solids - Non-GMP |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical structure identification | ✅ | ✅ |
| 1D NMR (¹H, 2H, ¹³C, ¹⁵N, ¹⁹F, ³¹P) | ✅ | ➖ |
| 1D NMR (¹³C, ¹⁵N, ¹⁹F, ³¹P, 27Al, 29Si) | ➖ | ✅ |
| 2D NMR (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMQC, HSQC, HMBC, DOSY) | ✅ | ➖ |
| Determination of purity (qNMR) | ✅ | ✅ |
| Primary reference-material (PRM) verification | ✅ | ➖ |
| Compendial NMR methods (USP, EP, JP) — verification & execution | ✅ | ➖ |
| Qualitative / quantitative NMR method development, validation, release testing, transfer | ✅ | ✅ non-GMP R&D / characterization only |
| Characterization of polymorphs, solvates, salts, cocrystals, amorphous forms | ➖ | ✅ |
| Identification of a generic API | ✅ | ✅ |
| Patent prosecution & litigation support (expert testimony, prior art) | ✅ | ✅ |
| Chemical-exchange analysis | ✅ | ✅ |
| Comparability / biosimilarity studies (biologics) | ✅ | ➖ |
| Confirm molecules per asymmetric unit | ➖ | ✅ |
| Conformational & structural analysis | ✅ | ✅ |
| Excipients identity confirmation | ✅ | ➖ |
| Formulation analysis / deformulation | ✅ | ✅ |
| Impurity & contaminant ID / quantitation | ✅ | ✅ |
| Molecular-mobility analysis | ✅ | ✅ |
| Product-failure analysis | ✅ | ✅ |
| Stereoisomer analysis | ✅ | ➖ |
Our Instruments and Capabilities:
| Application AND Technique Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| By studying the peaks of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra, the structure of many compounds can be determined. It can be a very selective technique, distinguishing among many atoms within a molecule or collection of molecules of the same type but which differ only in terms of their local chemical environment. NMR spectroscopy is used to unambiguously identify known and novel compounds. All isotopes that contain an odd number of protons and/or neutrons have an intrinsic nuclear magnetic moment and angular momentum, in other words a nonzero nuclear spin, while all nuclides with even numbers of both have a total spin of zero. The most commonly used nuclei are 1 H and 13 C. | ||
| Instrument | Models, Probes, Software | Additional Info |
| Bruker |
400MHZ ultrashield, Avance AVII cGMP and non cGMP Liquids, multi-nuclear (1H, 13C, 31P, 19F, 15N, and others with broadband probe) non cGMP Solids, multi-nuclear (13C, 31P, and 19F and others with broadband probe) Topspin 3.2 Software as well as multiple spectral analysis software packages 600, 800MHz |

In support of The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) General Chapter <761> Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and other Compendial chapters (e.g., <1761>), Triclinic Labs offers multi-dimensional cGMP liquids analysis with a broadband probe allowing for a myriad of experiments (1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, 31P, etc.) at variable temperatures (233 - 350K). |
How does NMR work?
When nuclei are placed into a magnetic field, their magnetic moment (spin) becomes aligned with the magnetic field. NMR uses a pulse of radio frequency energy to deflect the nuclei. When the energy is removed, the nuclei relax back to their original state and emit an electromagnetic pulse. A coil inside the NMR receives this RF pulse, and a computer transforms the signal into a spectral graph, which can be interpreted by a spectroscopist. Each nucleus that resides in a unique chemical environment, based upon the chemical structure, translates into a peak in the NMR spectrum. Its peak position (x-axis chemical shift value) and the multiplicity of the peak tells the scientist about its environment. The area of the peak corresponds to the number of nuclei producing the signal so this relationship allows for quantitative analysis.
A combination of 1-dimensional and 2-dimensional NMR experiments are usually necessary for complete confidence in complex chemical structures. The process of discerning structure typically involves:
-
1-dimensional proton ¹H-NMR and Carbon NMR are used to confirm the number of hydrogens and carbons in the
molecule, respectively.
-
¹H-¹H Correlation Spectroscopy (COSY) identifies the correlation between hydrogens
- ¹H-¹³C Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence Spectroscopy (HSQC) identifies which hydrogens are attached to which carbon atoms.
- ¹H-¹³C Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Correlation Spectroscopy (HMBC) shows the correlations between protons and carbons with multiple bonds
-
Other nuclei may be explored (e.g. 19F, 15N, 31P)

Pharmaceutical Applications
Uses of NMR in Current Guidance for Pharmaceutical Quality/CMC
Under current regulations in the United States, use of a human drug product not previously authorized for
marketing in the United States requires the submission of an IND to the Agency. FDA's regulations at 21 CFR
312.22 and 312.23, respectively, contain the general principles underlying the IND submission and the general
requirements for content and format. Section 312.23(a)(7)(i) requires that an IND for each phase of
investigation include sufficient Chemistry Manufacturing and Controls (CMC) information to ensure the proper
identity, strength or potency, quality, and purity of the drug substance and drug product. The FDA or other
regulatory agencies usually require full structural characterization by NMR. This data provides crucial
evidence of compound identity.
Other CMC Services we offer:
- Chemical name
- Structure figure
- Molecular formula
- Molecular weight
- Elemental analysis (CHN)
- UV/VIS spectroscopy
- IR spectroscopy
- Raman spectroscopy
- 1H NMR spectroscopy
- 13C NMR spectroscopy
- Mass spectrometry
- Optical, Specific rotation
- Phase identification by XRPD
- Ion Chromatography
- Single crystal X-ray
See a complete description of our CMC services. Click here.
Quantitative NMR
Quantitative NMR, or qNMR, is used for determination of concentration and purity of small molecules, for example. The qNMR method only requires that (a) the sample dissolves completely in a (normally fully deuterated) solvent, and (b) it contains NMR-active nuclides.
There are two broad categories of qNMR experiments: those used to determine the analyte concentration, and those used to determine a compound's purity.
Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Spectroscopy Services
- qNMR can provide fast and low-cost quality control (QC) tests such as identification, purity and potency tests, without the corresponding reference standard materials.
- qNMR is also useful in investigation of unknowns and product failure.
What is qNMR?
NMR spectroscopy analyzes molecules at the atomic level, detecting protons or carbons, making NMR one of the
most universal techniques. qNMR takes advantage of the fact that the peak area (integration) in NMR
spectroscopy is directly proportional to the concentration of the specific component in solution. This feature
allows for determination of relative concentration of each component in a mixture. For absolute quantitation,
a certified reference material (CRM) is utilized either as an internal or external standard. The CRM is not
chemically related to any of the components in question and therefore the same CRM can be used for
quantitation of wide variety of test articles.
Why qNMR?
NMR spectroscopy is one of the most universal techniques used in identification of chemical components. qNMR is a relatively simple but versatile technique that can perform the identification testing and simultaneously determine the concentration of one or more components in a test article without having the requirement of certified reference standard materials of each of the corresponding compounds. qNMR can be used for purity assay, potency determinations, investigation of unknowns, investigation of product failures, and as a part of quality control (QC) tests.
qNMR and Regulatory Requirements
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) chapter <761> Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy describes qNMR
under Qualitative Applications. For absolute quantitation, a CRM is used as an internal or an external
standard. The internal standard is co-dissolved in the solution with test articles. The external standard
solution is placed in an insert within the NMR tube that contains the test solution. The CRM is not
chemically related to any of the components in question. This simplifies the GMP validation procedure since
a limited number of CRM in a small number of solvents can be validated for linearity, range, accuracy,
precision, quantitation limit and robustness. For each new test article, only specificity needs to be
validated as long as the same solvent system and experimental parameters are used.
Pros and Cons of qNMR
Pros of qNMR:Cons of qNMR:
- qNMR is a primary method where the signal intensity depends directly on the number of protons and concentration.
- Quick and simple analysis of test articles to identify and quantify components. Quantitative information such as purity of drug substances, potency of drug products can be obtained by qNMR.
- Unlike chromatographic methods, reference standard materials of the corresponding compounds are not required. This is especially advantageous during drug product development when reference standards of the active ingredients and impurities are not available.
- Unlike HPLC-UV methods, there is no response factor calculation required for active ingredients and impurities.
- Unlike HPLC methods, water or volatile content analysis (by KF or TGA) are not required for the purity determination.
- A number of CRM are commercially available.
- Applied to components with known chemical structures.
- The CRM selected must have a specificity against the NMR peaks related to the test sample.
- The test article must have detectable nuclei (such as proton or carbon).
- For mixture analysis, all components of interest must be soluble in a deuterated solvent or solvents.
Applications of qNMR
- Identification and purity testing of pure components such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
- Identification and potency testing of drug product intermediates during product development and stability testing.
- Identification and potency testing, as a part of a release and stability study, of drug product intermediates and final products such as tablets, capsules, solutions, suspensions, granules, and powders.
- Concentration determination of each component in mixtures. The mixtures can be solids, solutions or suspensions.
- Investigation of product failure
- Food sciences

Mini Case Study:
qNMR Potency Testing of Generic Excedrin Tablets
Three different generic brands claiming equivalence to Excedrin Migraine Tablets were dissolved in DMSO-d6 with maleic acid as an internal standard. The label claims were evaluated and are provided in the table below. None of the generics we tested matched the label claims.
| Components | Dosage Label Claim (mg/tablet) |
Actual Dosage
Product 1 |
Actual Dosage
Product 2 |
Actual Dosage
Product 3 |
| Acetaminophen | 250 | 98% | 83% | 110% |
| Aspirin | 250 | 101% | 98% | 66% |
| Caffeine | 65 | 115% | 115% | 107% |
| Comments | Contains Salicylic acid (See Figure Below) |
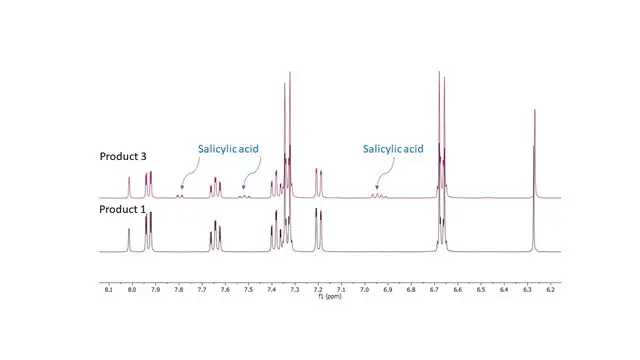
Figure 1. Salicylic acid is an active metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), which acts in part as a
prodrug to salicylic acid, it is probably best known for its use as a key ingredient in topical anti-acne
products.
Frequently Asked Questions about Triclinic Labs' NMR Spectroscopy Services
What types of NMR spectroscopy does Triclinic Labs offer?
Triclinic Labs provides both 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy services. This includes 1D ¹H and ¹³C NMR spectroscopy, as well as 2D techniques such as COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMQC, HSQC, and HMBC. These services are available for routine analyses and detailed structural elucidation.
Does Triclinic Labs offer cGMP-compliant NMR services?
Yes, Triclinic Labs offers cGMP-compliant NMR services, including method development, validation, and release testing. These services support regulatory requirements and are conducted using validated instruments and software compliant with FDA regulations.
What sample types can be analysed using Triclinic Labs' NMR services?
Triclinic Labs' NMR services can analyse a wide range of sample types, including small molecules, polymers, biomolecules, pharmaceuticals, and environmental samples, in both solid and liquid states.
Can Triclinic Labs assist with impurity identification and quantification?
Yes, Triclinic Labs offers services for the identification and quantification of impurities and contaminants in both solid and liquid samples, aiding in quality control and regulatory compliance.
Does Triclinic Labs provide support for patent prosecution and litigation?
Triclinic Labs offers expert services for patent prosecution and litigation support, including reproduction of prior art and expert testimony, leveraging their NMR spectroscopy capabilities.
What nuclei can be analysed using Triclinic Labs' NMR services?
Triclinic Labs' NMR services can analyse various nuclei, including ¹H, ¹³C, ¹⁵N, ¹⁹F, and ³¹P, providing comprehensive insights into molecular structures.
Can Triclinic Labs perform quantitative NMR analyses?
Yes, Triclinic Labs offers both qualitative and quantitative NMR method development, validation, release testing, and method transfer services to meet various analytical needs.
Does Triclinic Labs offer deformulation analysis using NMR?
Triclinic Labs provides deformulation analysis of both solid and liquid formulations using NMR spectroscopy, including identity confirmation of excipients used in pharmaceutical formulations.
Can Triclinic Labs analyse stereoisomers using NMR?
Yes, Triclinic Labs offers analysis of stereoisomers in both solid and liquid samples using NMR spectroscopy, aiding in the determination of stereochemistry and conformational analysis.
How can I contact Triclinic Labs for more information or to request a quote?
You can contact Triclinic Labs by visiting their contact page at https://tricliniclabs.com/company-information/contact-triclinic-labs-for-more-information-or-quote.html to request more information or a quote for their services.
